# How is Dew Point Calculated?
## Understanding Dew Point
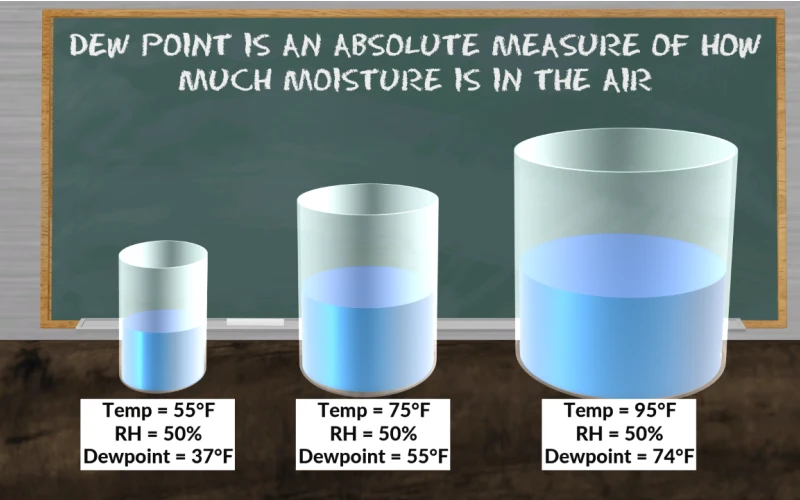
Dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, frost, or fog. It’s a crucial measurement in meteorology, HVAC systems, and various industrial processes. Unlike relative humidity, which changes with temperature, dew point provides a more consistent measure of atmospheric moisture.
## The Basic Formula
The most common method for calculating dew point is the Magnus formula:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
– Td is the dew point temperature
– T is the air temperature in °C
– RH is the relative humidity (expressed as a decimal, e.g., 50% = 0.5)
– a and b are Magnus coefficients (a = 17.27, b = 237.7°C)
– α(T,RH) = (a × T)/(b + T) + ln(RH)
## Step-by-Step Calculation
Let’s break down the calculation process:
1. Convert relative humidity from percentage to decimal form (divide by 100)
2. Calculate the intermediate value α(T,RH)
3. Plug the values into the dew point formula
4. Solve for Td
### Example Calculation
For air at 25°C with 60% relative humidity:
1. RH = 0.60
2. α = (17.27 × 25)/(237.7 + 25) + ln(0.60) ≈ 1.625 + (-0.511) ≈ 1.114
3. Td = (237.7 × 1.114)/(17.27 – 1.114) ≈ 264.8/16.156 ≈ 16.4°C
## Alternative Methods
### Psychrometric Chart Method
For quick estimations, professionals often use psychrometric charts:
1. Locate the dry-bulb temperature on the horizontal axis
2. Find the relative humidity curve
3. Follow horizontally to the saturation curve
4. Read the dew point temperature
### Online Calculators and Apps
Many digital tools can instantly calculate dew point when you input temperature and humidity values. These typically use more complex algorithms that account for atmospheric pressure and other factors.
## Factors Affecting Dew Point Accuracy
Several variables can influence dew point calculations:
– Atmospheric pressure (standard calculations assume sea level)
– Measurement accuracy of temperature and humidity
– Local environmental conditions
– Time of day (diurnal temperature variations)
## Practical Applications
Understanding dew point is essential for:
– Weather forecasting
– Preventing condensation in buildings
– Industrial drying processes
– Agricultural planning
– Aviation safety
– Museum climate control
## Conclusion
While the Magnus formula provides a good approximation for most purposes, remember that more precise calculations may require additional variables and complex equations. For everyday use, the basic method described here will give you reliable dew point estimates to help understand moisture conditions in your environment.
Keyword: how is dew point calculated